What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee Replacement (Total or Partial) is a surgical procedure where worn-out or damaged parts of the knee joint are replaced with artificial implants. It’s most commonly advised for patients suffering from osteoarthritis, knee deformity, or chronic pain that hasn’t improved with conservative treatment.
we combine the expertise of highly trained orthopedic surgeons with modern technology to deliver safer,
faster, and more comfortable knee replacement surgeries.
When You Might Need a Knee Replacement
knee pain that limits daily tasks Loss of mobility despite physiotherapy or medication Stiffness or swelling that doesn’t improve with rest Bow-legged or knock-knee deformity caused by joint damage Confirmed end-stage arthritis via diagnostic imaging
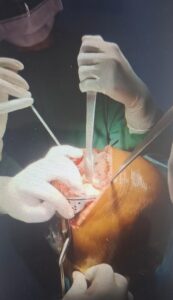
Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a worn or severely damaged knee joint is replaced with a carefully designed artificial implant. It’s often the preferred treatment for advanced arthritis, traumatic injury, or long-standing joint pain that no longer
How We Perform Total Knee Replacement
Complete health and mobility assessment Advanced imaging to customize the surgical plan Patient education on procedure, recovery, and expected outcomes
During Surgery
Careful removal of worn cartilage and damaged bone Insertion of a durable prosthetic joint tailored to fit the patient Correcting alignment for smooth, natural movement
After Surgery
Pain relief measures and early walking exercises Supervised physiotherapy to rebuild strength and range of motion Regular follow-ups to ensure optimal healing
Your Recovery Timeline :
Why Do Knees Hurt?
Knee pain is often the result of underlying mechanical or structural problems. Common causes include:
Sprains or tears in the knee ligaments (ACL, MCL, PCL, LCL)
Meniscus injuries from twisting or overexertion
Progressive joint damage from osteoarthritis
Autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis
Inflammation of the tendons or bursae (tendonitis/bursitis)
Accidents, high-impact trauma, or sports-related injuries
Poor body mechanics or excess weight adding pressure on joints
Signs may include swelling, instability, stiffness, or reduced range of motion, which require prompt medical assessment.
